Week5: Simulations of Protein: Cellular process and common tools in whole cell modeling
1.Whole-Cell Modeling: An Overview
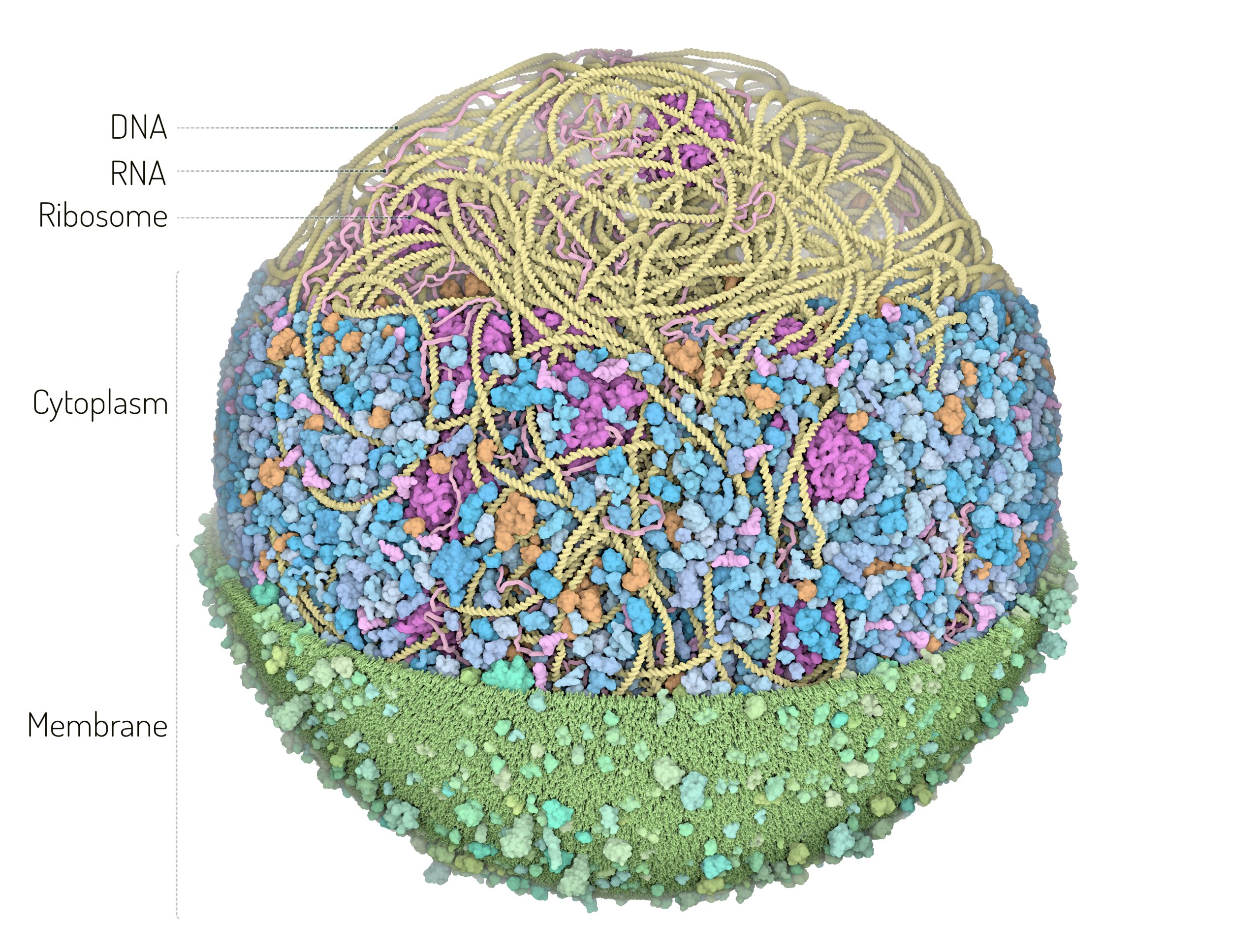
image source https://ccsb.scripps.edu/gallery/mycoplasma_model/
Definition & Goal:
Whole‐cell modeling (WCM) seeks to computationally simulate all the biochemical and biophysical processes within a living cell—from metabolism and gene expression to DNA replication and cell division—in a unified framework. The ultimate goal is to predict phenotype from genotype and provide a “virtual cell” that can be used to explore how cells grow, divide, and respond to perturbations.
Key Features:
- Integration Across Scales: WCM spans multiple time and length scales, capturing fast biochemical reactions alongside slower cellular processes.
- Hybrid Approaches: Most models combine deterministic methods (e.g., ordinary differential equations for metabolism) with stochastic simulations (e.g., for transcription or translation) and spatial diffusion (via PDEs or Brownian dynamics).
- Data-Driven Modeling: These models are grounded in diverse experimental data—from cryo-electron tomography (for spatial cell architecture) to omics and proteomics (for enzyme and gene expression levels).
2.Common Tools and Frameworks in Whole-Cell Modeling
Several software platforms and computational frameworks have been developed to aid in building and simulating whole‐cell models. Some of the widely used ones include:
Certainly! Here are some widely used tools and frameworks in whole-cell modeling, along with their respective links:
-
Lattice Microbes:
Often employed for simulating reaction-diffusion systems at the molecular level in a spatially resolved manner.
https://scs.illinois.edu/schulten/lm/ -
Virtual Cell (VCell):
An open-source platform that converts biological schematics into systems of differential equations. It supports both spatial and compartmental simulations and is used for modeling reaction kinetics, transport, and diffusion.
https://vcell.org/ -
COPASI:
A GUI-based tool for deterministic and stochastic simulation of biochemical networks, parameter estimation, and metabolic control analysis.
http://copasi.org/ -
libRoadRunner:
A high-performance library designed for SBML-based simulations, useful for dynamic and steady-state analysis.
https://libroadrunner.org/ -
Vivarium & PhysiCell:
Modern frameworks that enable hybrid multiscale simulations by coupling different submodels (e.g., reaction-diffusion, mechanical interactions) within a cell or tissue.- Vivarium: https://vivarium-collective.github.io/
- PhysiCell: http://physicell.org/
These tools provide a range of capabilities for modeling and simulating complex biological systems, each with its unique features and strengths.
These tools leverage various numerical methods (ODE/PDE solvers, stochastic algorithms, Brownian dynamics) and allow researchers to integrate heterogeneous experimental data into a cohesive computational model.